User Tools
Sidebar
This is an old revision of the document!
Dan's Wiki/Research Journal
This Wiki is a dedicated space for documenting my projects and research!
Hypervisor Performace
Jan 28, 2014
I have decided to document the setup, usage, and performace differences of multiple hypervisors. The intent of this document is to help other Lab46 users ch
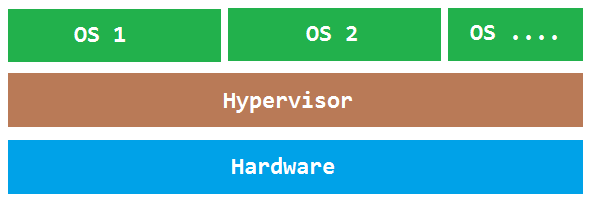
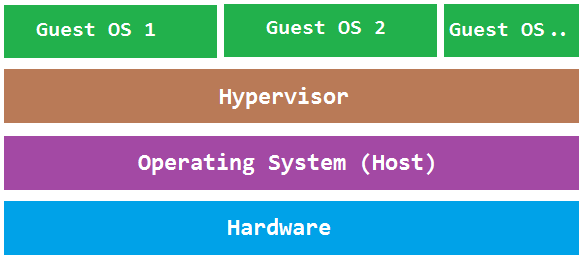
Hypervisors can be broken down into two types:
- Type-1: Native or bare metal hypervisors
- Type-2: Hosted hypervisors
Type-1
Type-1 hypervisors run directly on the host hardware allowing for hardware control and guest OS managability. Guest operating systmes are then run as processes on the host.
Examples of Type-1 hypervisors:
Type-2
Type-2 hypervisors run on top of existing operating systems much like web browsers or email clients. the hypervisor is then completely dependent upon the host operating system for its functionality.
Examples of Type-2 hypervisors:
Basic System Overview
To get this project going i decided to use one of my personal servers. This is the system i will be using for all testing as to keep a consistent approach to each hypervisor i test. System:
- Opteron 1385 Quadcore CPU
- 16GB of 800mhz DDR2
- 6x1TB 7200RPM HDDs
- Software Raid 10
OS:
- Debian 8 (Jessie)
Installation of KVM
The first hypervisor i will be testing is KVM (Kernal Based Virtual Machine)
Step 1. Install KVM & Libvirt from Debian Repository
apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-bin
Step 2. To be able to manage virtual machines as a non-root user we will need to add our account to the groups kvm and libvirt
adduser "username" kvm adduser "username" libvirt
Thats it! Now KVM is ready!
Management Options
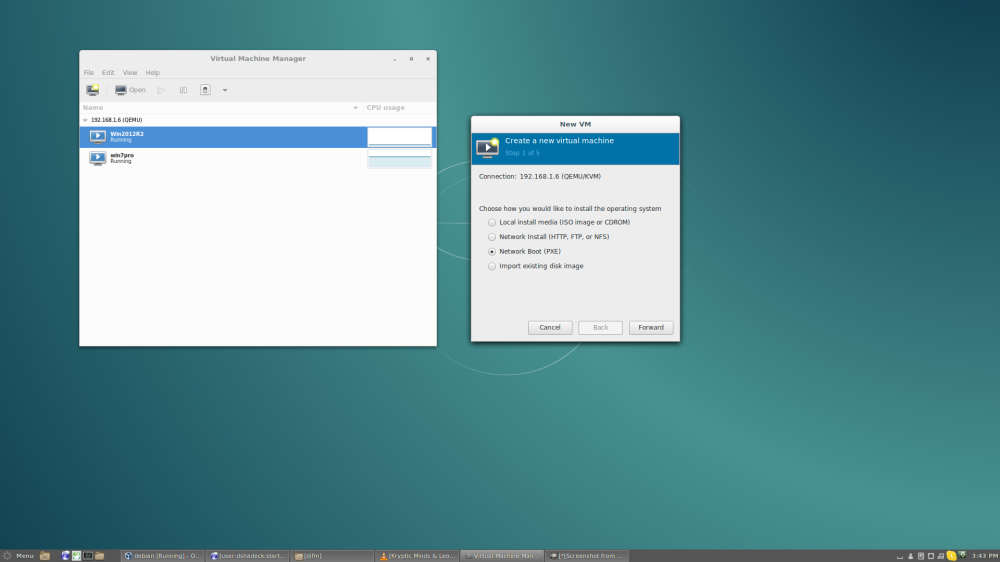
KVM can be managed in multiple ways. The most popular approach is mgmt directly from the Linux CLI using virsh. (This is why we installed Libvirt)
duder@hyper1:~$ sudo virsh --connect qemu:///system
Welcome to virsh, the virtualization interactive terminal.
Type: 'help' for help with commands
'quit' to quit
virsh # list --all
Id Name State
----------------------------------------------------
2 win7pro running
3 Win2012R2 running
virsh #
duder@hyper1:~$ kvm -help
QEMU emulator version 2.1.2 (Debian 1:2.1+dfsg-11), Copyright (c) 2003-2008 Fabrice Bellard
usage: qemu-system-x86_64 [options] [disk_image]
'disk_image' is a raw hard disk image for IDE hard disk 0
Standard options:
-h or -help display this help and exit
-version display version information and exit
-machine [type=]name[,prop[=value][,...]]
selects emulated machine ('-machine help' for list)
property accel=accel1[:accel2[:...]] selects accelerator
supported accelerators are kvm, xen, tcg (default: tcg)
kernel_irqchip=on|off controls accelerated irqchip support
kvm_shadow_mem=size of KVM shadow MMU
dump-guest-core=on|off include guest memory in a core dump (default=on)
mem-merge=on|off controls memory merge support (default: on)
-cpu cpu select CPU ('-cpu help' for list)
-smp [cpus=]n[,maxcpus=cpus][,cores=cores][,threads=threads][,sockets=sockets]
set the number of CPUs to 'n' [default=1]
maxcpus= maximum number of total cpus, including
offline CPUs for hotplug, etc
cores= number of CPU cores on one socket
threads= number of threads on one CPU core
sockets= number of discrete sockets in the system
-numa node[,mem=size][,cpus=cpu[-cpu]][,nodeid=node]
-numa node[,memdev=id][,cpus=cpu[-cpu]][,nodeid=node]
-add-fd fd=fd,set=set[,opaque=opaque]
Add 'fd' to fd 'set'
-set group.id.arg=value
set <arg> parameter for item <id> of type <group>
i.e. -set drive.$id.file=/path/to/image
-global driver.prop=value
set a global default for a driver property
-boot [order=drives][,once=drives][,menu=on|off]
[,splash=sp_name][,splash-time=sp_time][,reboot-timeout=rb_time][,strict=on|off]
'drives': floppy (a), hard disk (c), CD-ROM (d), network (n)
'sp_name': the file's name that would be passed to bios as logo picture, if menu=on
'sp_time': the period that splash picture last if menu=on, unit is ms
'rb_timeout': the timeout before guest reboot when boot failed, unit is ms
-m[emory] [size=]megs[,slots=n,maxmem=size]
configure guest RAM
size: initial amount of guest memory (default: 128MiB)
slots: number of hotplug slots (default: none)
maxmem: maximum amount of guest memory (default: none)
-mem-path FILE provide backing storage for guest RAM
-mem-prealloc preallocate guest memory (use with -mem-path)
-k language use keyboard layout (for example 'fr' for French)
-audio-help print list of audio drivers and their options
-soundhw c1,... enable audio support
and only specified sound cards (comma separated list)
use '-soundhw help' to get the list of supported cards
use '-soundhw all' to enable all of them
-balloon none disable balloon device
-balloon virtio[,addr=str]
enable virtio balloon device (default)
-device driver[,prop[=value][,...]]
add device (based on driver)
prop=value,... sets driver properties
use '-device help' to print all possible drivers
use '-device driver,help' to print all possible properties
-name string1[,process=string2][,debug-threads=on|off]
set the name of the guest
string1 sets the window title and string2 the process name (on Linux)
When debug-threads is enabled, individual threads are given a separate name (on Linux)
NOTE: The thread names are for debugging and not a stable API.
-uuid %08x-%04x-%04x-%04x-%012x
specify machine UUID
Block device options:
-fda/-fdb file use 'file' as floppy disk 0/1 image
-hda/-hdb file use 'file' as IDE hard disk 0/1 image
-hdc/-hdd file use 'file' as IDE hard disk 2/3 image
-cdrom file use 'file' as IDE cdrom image (cdrom is ide1 master)
-drive [file=file][,if=type][,bus=n][,unit=m][,media=d][,index=i]
[,cyls=c,heads=h,secs=s[,trans=t]][,snapshot=on|off]
[,cache=writethrough|writeback|none|directsync|unsafe][,format=f]
[,serial=s][,addr=A][,rerror=ignore|stop|report]
[,werror=ignore|stop|report|enospc][,id=name][,aio=threads|native]
[,readonly=on|off][,copy-on-read=on|off]
[,discard=ignore|unmap][,detect-zeroes=on|off|unmap]
[[,bps=b]|[[,bps_rd=r][,bps_wr=w]]]
[[,iops=i]|[[,iops_rd=r][,iops_wr=w]]]
[[,bps_max=bm]|[[,bps_rd_max=rm][,bps_wr_max=wm]]]
[[,iops_max=im]|[[,iops_rd_max=irm][,iops_wr_max=iwm]]]
[[,iops_size=is]]
use 'file' as a drive image
-mtdblock file use 'file' as on-board Flash memory image
-sd file use 'file' as SecureDigital card image
-pflash file use 'file' as a parallel flash image
-snapshot write to temporary files instead of disk image files
-hdachs c,h,s[,t]
force hard disk 0 physical geometry and the optional BIOS
translation (t=none or lba) (usually QEMU can guess them)
-fsdev fsdriver,id=id[,path=path,][security_model={mapped-xattr|mapped-file|passthrough|none}]
[,writeout=immediate][,readonly][,socket=socket|sock_fd=sock_fd]
-virtfs local,path=path,mount_tag=tag,security_model=[mapped-xattr|mapped-file|passthrough|none]
[,writeout=immediate][,readonly][,socket=socket|sock_fd=sock_fd]
-virtfs_synth Create synthetic file system image
USB options:
-usb enable the USB driver (will be the default soon)
-usbdevice name add the host or guest USB device 'name'
Display options:
-display sdl[,frame=on|off][,alt_grab=on|off][,ctrl_grab=on|off]
[,window_close=on|off]|curses|none|
gtk[,grab_on_hover=on|off]|
vnc=<display>[,<optargs>]
select display type
-nographic disable graphical output and redirect serial I/Os to console
-curses use a curses/ncurses interface instead of SDL
-no-frame open SDL window without a frame and window decorations
-alt-grab use Ctrl-Alt-Shift to grab mouse (instead of Ctrl-Alt)
-ctrl-grab use Right-Ctrl to grab mouse (instead of Ctrl-Alt)
-no-quit disable SDL window close capability
-sdl enable SDL
-spice [port=port][,tls-port=secured-port][,x509-dir=<dir>]
[,x509-key-file=<file>][,x509-key-password=<file>]
[,x509-cert-file=<file>][,x509-cacert-file=<file>]
[,x509-dh-key-file=<file>][,addr=addr][,ipv4|ipv6]
[,tls-ciphers=<list>]
[,tls-channel=[main|display|cursor|inputs|record|playback]]
[,plaintext-channel=[main|display|cursor|inputs|record|playback]]
[,sasl][,password=<secret>][,disable-ticketing]
[,image-compression=[auto_glz|auto_lz|quic|glz|lz|off]]
[,jpeg-wan-compression=[auto|never|always]]
[,zlib-glz-wan-compression=[auto|never|always]]
[,streaming-video=[off|all|filter]][,disable-copy-paste]
[,disable-agent-file-xfer][,agent-mouse=[on|off]]
[,playback-compression=[on|off]][,seamless-migration=[on|off]]
enable spice
at least one of {port, tls-port} is mandatory
-portrait rotate graphical output 90 deg left (only PXA LCD)
-rotate <deg> rotate graphical output some deg left (only PXA LCD)
-vga [std|cirrus|vmware|qxl|xenfb|tcx|cg3|none]
select video card type
-full-screen start in full screen
-vnc display start a VNC server on display
i386 target only:
-win2k-hack use it when installing Windows 2000 to avoid a disk full bug
-no-fd-bootchk disable boot signature checking for floppy disks
-no-acpi disable ACPI
-no-hpet disable HPET
-acpitable [sig=str][,rev=n][,oem_id=str][,oem_table_id=str][,oem_rev=n][,asl_compiler_id=str][,asl_compiler_rev=n][,{data|file}=file1[:file2]...]
ACPI table description
-smbios file=binary
load SMBIOS entry from binary file
-smbios type=0[,vendor=str][,version=str][,date=str][,release=%d.%d][,uefi=on|off]
specify SMBIOS type 0 fields
-smbios type=1[,manufacturer=str][,product=str][,version=str][,serial=str]
[,uuid=uuid][,sku=str][,family=str]
specify SMBIOS type 1 fields
Network options:
-net nic[,vlan=n][,macaddr=mac][,model=type][,name=str][,addr=str][,vectors=v]
create a new Network Interface Card and connect it to VLAN 'n'
-net user[,vlan=n][,name=str][,net=addr[/mask]][,host=addr][,restrict=on|off]
[,hostname=host][,dhcpstart=addr][,dns=addr][,dnssearch=domain][,tftp=dir]
[,bootfile=f][,hostfwd=rule][,guestfwd=rule][,smb=dir[,smbserver=addr]]
connect the user mode network stack to VLAN 'n', configure its
DHCP server and enabled optional services
-net tap[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,fds=x:y:...:z][,ifname=name][,script=file][,downscript=dfile][,helper=helper][,sndbuf=nbytes][,vnet_hdr=on|off][,vhost=on|off][,vhostfd=h][,vhostfds=x:y:...:z][,vhostforce=on|off][,queues=n]
connect the host TAP network interface to VLAN 'n'
use network scripts 'file' (default=/etc/qemu-ifup)
to configure it and 'dfile' (default=/etc/qemu-ifdown)
to deconfigure it
use '[down]script=no' to disable script execution
use network helper 'helper' (default=/usr/lib/qemu/qemu-bridge-helper) to
configure it
use 'fd=h' to connect to an already opened TAP interface
use 'fds=x:y:...:z' to connect to already opened multiqueue capable TAP interfaces
use 'sndbuf=nbytes' to limit the size of the send buffer (the
default is disabled 'sndbuf=0' to enable flow control set 'sndbuf=1048576')
use vnet_hdr=off to avoid enabling the IFF_VNET_HDR tap flag
use vnet_hdr=on to make the lack of IFF_VNET_HDR support an error condition
use vhost=on to enable experimental in kernel accelerator
(only has effect for virtio guests which use MSIX)
use vhostforce=on to force vhost on for non-MSIX virtio guests
use 'vhostfd=h' to connect to an already opened vhost net device
use 'vhostfds=x:y:...:z to connect to multiple already opened vhost net devices
use 'queues=n' to specify the number of queues to be created for multiqueue TAP
-net bridge[,vlan=n][,name=str][,br=bridge][,helper=helper]
connects a host TAP network interface to a host bridge device 'br'
(default=br0) using the program 'helper'
(default=/usr/lib/qemu/qemu-bridge-helper)
-net l2tpv3[,vlan=n][,name=str],src=srcaddr,dst=dstaddr[,srcport=srcport][,dstport=dstport],txsession=txsession[,rxsession=rxsession][,ipv6=on/off][,udp=on/off][,cookie64=on/off][,counter][,pincounter][,txcookie=txcookie][,rxcookie=rxcookie][,offset=offset]
connect the VLAN to an Ethernet over L2TPv3 pseudowire
Linux kernel 3.3+ as well as most routers can talk
L2TPv3. This transport allows connecting a VM to a VM,
VM to a router and even VM to Host. It is a nearly-universal
standard (RFC3391). Note - this implementation uses static
pre-configured tunnels (same as the Linux kernel).
use 'src=' to specify source address
use 'dst=' to specify destination address
use 'udp=on' to specify udp encapsulation
use 'dstport=' to specify destination udp port
use 'dstport=' to specify destination udp port
use 'ipv6=on' to force v6
L2TPv3 uses cookies to prevent misconfiguration as
well as a weak security measure
use 'rxcookie=0x012345678' to specify a rxcookie
use 'txcookie=0x012345678' to specify a txcookie
use 'cookie64=on' to set cookie size to 64 bit, otherwise 32
use 'counter=off' to force a 'cut-down' L2TPv3 with no counter
use 'pincounter=on' to work around broken counter handling in peer
use 'offset=X' to add an extra offset between header and data
-net socket[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,listen=[host]:port][,connect=host:port]
connect the vlan 'n' to another VLAN using a socket connection
-net socket[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,mcast=maddr:port[,localaddr=addr]]
connect the vlan 'n' to multicast maddr and port
use 'localaddr=addr' to specify the host address to send packets from
-net socket[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,udp=host:port][,localaddr=host:port]
connect the vlan 'n' to another VLAN using an UDP tunnel
-net vde[,vlan=n][,name=str][,sock=socketpath][,port=n][,group=groupname][,mode=octalmode]
connect the vlan 'n' to port 'n' of a vde switch running
on host and listening for incoming connections on 'socketpath'.
Use group 'groupname' and mode 'octalmode' to change default
ownership and permissions for communication port.
-net dump[,vlan=n][,file=f][,len=n]
dump traffic on vlan 'n' to file 'f' (max n bytes per packet)
-net none use it alone to have zero network devices. If no -net option
is provided, the default is '-net nic -net user'
-netdev [user|tap|bridge|vde|vhost-user|socket|hubport],id=str[,option][,option][,...]
Character device options:
-chardev null,id=id[,mux=on|off]
-chardev socket,id=id[,host=host],port=host[,to=to][,ipv4][,ipv6][,nodelay]
[,server][,nowait][,telnet][,mux=on|off] (tcp)
-chardev socket,id=id,path=path[,server][,nowait][,telnet],[mux=on|off] (unix)
-chardev udp,id=id[,host=host],port=port[,localaddr=localaddr]
[,localport=localport][,ipv4][,ipv6][,mux=on|off]
-chardev msmouse,id=id[,mux=on|off]
-chardev vc,id=id[[,width=width][,height=height]][[,cols=cols][,rows=rows]]
[,mux=on|off]
-chardev ringbuf,id=id[,size=size]
-chardev file,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev pipe,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev pty,id=id[,mux=on|off]
-chardev stdio,id=id[,mux=on|off][,signal=on|off]
-chardev braille,id=id[,mux=on|off]
-chardev serial,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev tty,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev parallel,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev parport,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev spicevmc,id=id,name=name[,debug=debug]
-chardev spiceport,id=id,name=name[,debug=debug]
Device URL Syntax:
-iscsi [user=user][,password=password]
[,header-digest=CRC32C|CR32C-NONE|NONE-CRC32C|NONE
[,initiator-name=initiator-iqn][,id=target-iqn]
iSCSI session parameters
Bluetooth(R) options:
-bt hci,null dumb bluetooth HCI - doesn't respond to commands
-bt hci,host[:id]
use host's HCI with the given name
-bt hci[,vlan=n]
emulate a standard HCI in virtual scatternet 'n'
-bt vhci[,vlan=n]
add host computer to virtual scatternet 'n' using VHCI
-bt device:dev[,vlan=n]
emulate a bluetooth device 'dev' in scatternet 'n'
TPM device options:
-tpmdev passthrough,id=id[,path=path][,cancel-path=path]
use path to provide path to a character device; default is /dev/tpm0
use cancel-path to provide path to TPM's cancel sysfs entry; if
not provided it will be searched for in /sys/class/misc/tpm?/device
Linux/Multiboot boot specific:
-kernel bzImage use 'bzImage' as kernel image
-append cmdline use 'cmdline' as kernel command line
-initrd file use 'file' as initial ram disk
-dtb file use 'file' as device tree image
Debug/Expert options:
-serial dev redirect the serial port to char device 'dev'
-parallel dev redirect the parallel port to char device 'dev'
-monitor dev redirect the monitor to char device 'dev'
-qmp dev like -monitor but opens in 'control' mode
-mon [chardev=]name[,mode=readline|control][,default]
-debugcon dev redirect the debug console to char device 'dev'
-pidfile file write PID to 'file'
-singlestep always run in singlestep mode
-S freeze CPU at startup (use 'c' to start execution)
-realtime [mlock=on|off]
run qemu with realtime features
mlock=on|off controls mlock support (default: on)
-gdb dev wait for gdb connection on 'dev'
-s shorthand for -gdb tcp::1234
-d item1,... enable logging of specified items (use '-d help' for a list of log items)
-D logfile output log to logfile (default stderr)
-L path set the directory for the BIOS, VGA BIOS and keymaps
-bios file set the filename for the BIOS
-enable-kvm enable KVM full virtualization support
-xen-domid id specify xen guest domain id
-xen-create create domain using xen hypercalls, bypassing xend
warning: should not be used when xend is in use
-xen-attach attach to existing xen domain
xend will use this when starting QEMU
-no-reboot exit instead of rebooting
-no-shutdown stop before shutdown
-loadvm [tag|id]
start right away with a saved state (loadvm in monitor)
-daemonize daemonize QEMU after initializing
-option-rom rom load a file, rom, into the option ROM space
-clock force the use of the given methods for timer alarm.
To see what timers are available use '-clock help'
-rtc [base=utc|localtime|date][,clock=host|rt|vm][,driftfix=none|slew]
set the RTC base and clock, enable drift fix for clock ticks (x86 only)
-icount [N|auto]
enable virtual instruction counter with 2^N clock ticks per
instruction
-watchdog i6300esb|ib700
enable virtual hardware watchdog [default=none]
-watchdog-action reset|shutdown|poweroff|pause|debug|none
action when watchdog fires [default=reset]
-echr chr set terminal escape character instead of ctrl-a
-virtioconsole c
set virtio console
-show-cursor show cursor
-tb-size n set TB size
-incoming p prepare for incoming migration, listen on port p
-nodefaults don't create default devices
-chroot dir chroot to dir just before starting the VM
-runas user change to user id user just before starting the VM
-sandbox <arg> Enable seccomp mode 2 system call filter (default 'off').
-readconfig <file>
-writeconfig <file>
read/write config file
-nodefconfig
do not load default config files at startup
-no-user-config
do not load user-provided config files at startup
-trace [events=<file>][,file=<file>]
specify tracing options
-enable-fips enable FIPS 140-2 compliance
-object TYPENAME[,PROP1=VALUE1,...]
create an new object of type TYPENAME setting properties
in the order they are specified. Note that the 'id'
property must be set. These objects are placed in the
'/objects' path.
-msg timestamp[=on|off]
change the format of messages
on|off controls leading timestamps (default:on)
-dump-vmstate <file>
Output vmstate information in JSON format to file.
Use the scripts/vmstate-static-checker.py file to
check for possible regressions in migration code
by comparing two such vmstate dumps.
During emulation, the following keys are useful:
ctrl-alt-f toggle full screen
ctrl-alt-n switch to virtual console 'n'
ctrl-alt toggle mouse and keyboard grab
When using -nographic, press 'ctrl-a h' to get some help.
Another approach is to use managment software. I currently use Virtual Machine Manager.